 A breakdown of the Kaseya ransomware attack and how Coretelligent successfully evaded any impacts.
A breakdown of the Kaseya ransomware attack and how Coretelligent successfully evaded any impacts.
The July 4th weekend Kaseya ransomware attack should be a warning to all organizations from small- and mid-sized businesses to multinational corporations. Not only did the attack compromise and exploit the Kaseya VSA product itself, but the hackers’ true focus and intention were to access as many downstream customers through the platform as possible to maximize the potential earnings from their ransomware attack. This kind of attack is referred to as a supply chain ransomware attack. In the Kaseya/REvilware ransomware incident, the hackers responsible for the attack hoped to magnify their results by targeting a service provider and gaining access to client’s systems. Unfortunately, in the eyes of cybercriminals, many ransomware victims are better than just one victim. More victims increase their chances of collecting on a significant cryptocurrency ransom demand, particularly within the realm of managed service providers and their downstream customers.
Shots Fired
While this is the most massive ransomware attack on record, it could have been much worse. Considering that the company is one of the largest in the remote monitoring landscape, the thousands of victims affected could have been tens of thousands. Today, Kaseya VSA users were the targets, but tomorrow it could be the customers of an even more popular vendor or Software-as-a-service (SaaS) provider. There is no enterprise in the world that does not utilize service providers as a regular part of their business—not to implicate any specific company, but think about the prevalence of Microsoft, Adobe, Amazon Web Services, Salesforce, Zoom, and many others. This incident indicates an escalation by cybercriminals, and we should all be paying attention. Sorry to say, but this is the proverbial shot fired across our bow, and now is the time is now to batten down the hatches for the next potential attack.
What Made Coretelligent Different?
Not all of Kaseya’s customers were impacted, however. Neither Coretelligent nor any of our clients were affected. At the same time, other MSPs and their customers were caught up in the Kaseya ransomware attack and locked out of their systems, awaiting backup restoration efforts or a decryption key. We credit this outcome to the fact that we do not rely on any single tool to provide our only means of security, and we have robust incident response planning and workflows to handle such an event. We have multiple layers of protection in place to protect our critical systems and data. Additionally, we were able to mobilize our team immediately upon news breaking of this event to take swift action to mitigate and protect until further information was available.
While not directly impacted, Coretelligent immediately enacted our Incident Response Plan out of an abundance of caution upon learning of the attack in progress on July 2nd. Doing so allowed us to eliminate any potential issues and keep all customers protected until further information on the attack became available. As leaders in the MSP space, we must follow the very same incident response guidance that we offer as recommendations to our clients.
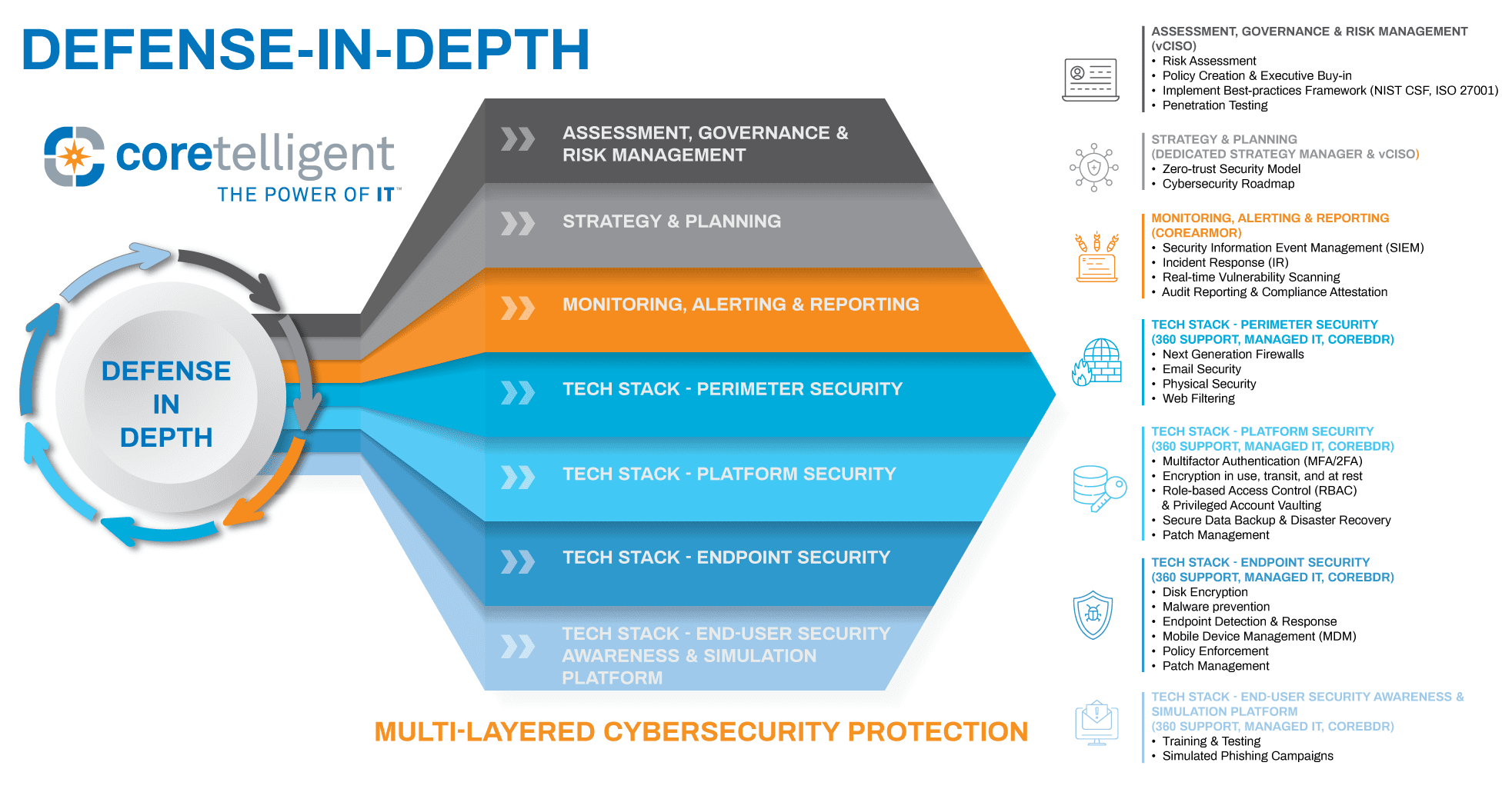
Coretelligent’s robust, multi-layered approach to cybersecurity, also referred to as defense-in-depth, protected us—and, more importantly, our clients.
Here are some of the key provisions that make up this layered defense model:
- Perimeter Security – Strong firewall policies to allow only necessary services access, security scanning (antimalware, antivirus), DNS/web filtering, Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDS/IPS), and geo-blocking all help reduce the ability of malicious actors to access services such as Kaseya that were public-facing.
- Multi-Factor Authentication – All critical services are secured with multi-factor authentication to reduce the possibility of unauthorized access due to compromised credentials.
- Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) – Coretelligent operates a tiered and segmented permission structure within our environment. Employees are granted the appropriate level of access to systems based on their role, responsibility, and seniority. This process helps to govern and restrict full administrative access to key systems and infrastructure to a select group of senior internal resources; as such, there are fewer accounts and avenues for attackers to gain access and do damage.
- Endpoint Protection – Coretelligent leverages SentinelOne Endpoint Protection for all our corporate servers and workstations. This platform, along with others, can detect/block these types of exploit attacks.
- Security Logging and Monitoring – All critical infrastructure is monitored in real-time via our CoreArmor platform. Logs and data are aggregated from all our critical systems to look for anomalous or suspicious behavior and immediately alert our team.
As Coretelligent’s infrastructure was protected with the provisions noted above, our customers were also still protected via endpoint security software from our other partner providers, SentinelOne and Webroot. In addition, subscribers to our CoreArmor service benefitted from additional real-time alerting and protections against this attack as the indicators of compromise (IOC) used in this attack were discovered and reported. This coverage allowed for security products to better detect and protect against this attack from further spreading or infection of new targets. All our key security vendors provided security updates and tracking information throughout this event to help block the ransomware and additional infected files to reduce further spread and infections.
The Plan You Hope You Never Have to Use
An Incident Response Plan is a set of guidelines and procedures put into effect during a security incident. Generally, this type of plan includes guidelines for the initial response, escalation, containment, and recovery or post-incident activities.
As our Incident Response Plan recommends, we quickly shut down all activity from the Kaseya compromised servers. In addition, we followed the additional steps outlined in our plan to safeguard our resources and those of our clients. As a result, neither Coretelligent nor any of our customers experienced any impacts—excluding inconvenience—as we proceeded through our Incident Response Plan. Additionally, to honor Coretelligent’s commitment to transparency, our team provided twice-daily email updates to our customers, which are also available in this blog post.
As the attack unfolded, Kaseya shared that the hackers were able to gain access through a zero-day. A zero-day is a previously unknown vulnerability discovered in software or system design that cyber criminals can exploit to gain entry to networks. A patch was released on July 13th to address the vulnerabilities, and after careful review of the fix, our Coretelligent engineers begin implementing the patch on July 14th.
Future Plans
Moving forward, Coretelligent will address any concerns we may have with Kaseya and provide an update and recommendation to our clients.
 Frequently Asked Questions About the Kaseya Ransomware Attack
Frequently Asked Questions About the Kaseya Ransomware Attack
What is Kaseya?
Kaseya is a leading provider of cloud-based IT management and security solutions for small, medium, and large businesses. The Kaseya VSA platform is just one tool that Coretelligent uses to help manage, access, and maintain customer servers and workstations.
How does Coretelligent use Kaseya?
Coretelligent uses Kaseya to remotely access, troubleshoot, monitor, and manage servers and endpoints of our customers and perform automation and maintenance activities for customers who subscribe to that service. Additionally, Coretelligent uses a combination of tools (Kaseya and LogicMonitor) to monitor customers who have signed up for proactive monitoring services.
Who is behind the ransomware attack?
This attack was perpetrated by the cybercriminal group known as the REvil Ransomware Gang. The threat actors were implicated in the June 2021 hack of the meat-processor JBS. After the JBS attack, the group warned that they would next target U.S. companies. As a result, the White House called for President Vladimir V. Putin to shut down the Russia-linked gang and other ransomware groups targeting the U.S.
How did Kaseya get hacked?
The attackers exploited four vulnerabilities in Kaseya’s VSA product to bypass authentication, upload ransomware, and other payloads, and then execute the malicious code/files. This vulnerability allowed the hackers to upload the malicious software, create Kaseya procedures (scripts) to copy files and execute the ransomware. They then executed these procedures against all customer agents tied to each Kaseya VSA server to start the ransomware attack and deliver a ransom note to downstream customers. They then removed logs and other forensic evidence to cover their tracks.
A more detailed technical breakdown is available at TrueSec.
Why were some Kaseya customers infected and others were not?
This question is not yet fully answered at this point, and more forensic details may still need to be shared from the impacted MSPs with Kaseya, law enforcement, and various security firms that are involved in this incident.
From what we can tell, customers utilizing multiple layers of protection were better protected against this attack. For example, Coretelligent uses perimeter firewalls, DNS filtering, geo-blocking, multi-factor authentication, and other security controls to protect our VSA servers. This practice, commonly referred to as defense in depth, provides multiple hurdles for an attacker to bypass, making for a more challenging target to crack. This approach may encourage the attacker to move on and works to protect Coretelligent and its customers.
Additionally, it should be noted that only premises customers, meaning those with on-premise VSA servers, were impacted.
Is it safe to use Kaseya now that it has been patched?
YES—our Kaseya VSA environment is safe and secured for use. Coretelligent successfully applied version 9.5.7.a patch, which resolved multiple security vulnerabilities in the product and has made all the necessary configuration adjustments and security recommendations to our Kaseya VSA servers as of July 13th.
Kaseya Help Desk Resources:
Our VSA servers continue to be protected by multiple security layers and restrictions, along with comprehensive security monitoring and alerting, which we believe will continue to keep our environment protected and secure.
Will Coretelligent continue to use Kaseya for Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM)?
Coretelligent will undergo a careful forensic review of this experience and decide whether to continue with Kaseya for remote monitoring and management or switch to a different vendor platform. In the interest of full transparency, we will communicate our decision with you, our customers, and provide background and justification about our decision.
How can we reduce the risk of this kind of supply chain attack?
Partnering with a tested, transparent, and expert managed service provider like Coretelligent is your best defense against ransomware and other cyberattacks. We offer best-in-class services covering a full range of technology needs with specialized expertise in cybersecurity.
What is the official response and guidance from the U.S. government?
The Deputy National Security Advisor Anne Neuberger has provided regular updates about the Kaseya ransomware attack and law enforcement is continuing its investigations to safeguard critical infrastructure and prevent future incidents. In an early statement about the attack, she remarked that President Joe Biden had “directed the full resources of the government to investigate this incident.”
Additionally, the Cybersecurity Infrastructure Security Agency, one of the federal agencies tasked with protecting U.S. assets, released a CISA guidance advisory which included a multitude of recommendations for hardening IT systems, including:
- Using authentication process controls, like multi-factor authentication, the use of which might have saved the Colonial Pipeline from getting hacked.
- Adhere to best practices for password and permission management
- Regularly update software and operating systems
- Employ a backup solution to automatically and continuously back up critical data and systems. Store backups in an easily retrievable location that is air-gapped from the organizational network.
Comprehensive Cybersecurity Protection
For more recommendations and information about how Coretelligent’s cybersecurity practices and solutions can protect your organization from incidents like the Kaseya ransomware attack, reach out to schedule your complimentary initial consultation. Coretelligent also offers expertise working with specific industries that have cybersecurity compliance requirements like financial services, life sciences, real estate investment, and others.
Think About It with Chris Messer, CTO
 As Chief Technology Officer, Chris Messer is a transformational and strategic IT leader who establishes and leads Coretelligent’s technical vision and technological development. Chris shares a post each month called Think About It.
As Chief Technology Officer, Chris Messer is a transformational and strategic IT leader who establishes and leads Coretelligent’s technical vision and technological development. Chris shares a post each month called Think About It.
Click here to learn more about Chris.
 Yesterday, the Cybersecurity Infrastructure & Security Agency (CISA), the federal agency charged with protecting the nation’s cyber infrastructure, released a notice from the National Cyber Awareness System. Based on recent malicious cyber incidents in Ukraine, CISA urges organizations across all sectors and of any size to be on alert for malicious cyber activity. The agency also provided a checklist of actions to take immediately.
Yesterday, the Cybersecurity Infrastructure & Security Agency (CISA), the federal agency charged with protecting the nation’s cyber infrastructure, released a notice from the National Cyber Awareness System. Based on recent malicious cyber incidents in Ukraine, CISA urges organizations across all sectors and of any size to be on alert for malicious cyber activity. The agency also provided a checklist of actions to take immediately.


 Disasters and cyber-attacks happen, but data loss does not have to be inevitable. Data loss can be
Disasters and cyber-attacks happen, but data loss does not have to be inevitable. Data loss can be 

 Though it’s been around for a while, phishing attacks continue to be one the most common attacks and a favorite among hackers for their effectiveness and simplicity. These types of malicious attacks account for 90% of all data breaches.
Though it’s been around for a while, phishing attacks continue to be one the most common attacks and a favorite among hackers for their effectiveness and simplicity. These types of malicious attacks account for 90% of all data breaches.
 Reducing your organization’s risk from cyber threats requires a holistic approach. Cybersecurity should be integrated across all divisions and at all levels. Cybercriminals do not recognize your internal organization or care about job titles but seek to exploit any weaknesses they discover.
Reducing your organization’s risk from cyber threats requires a holistic approach. Cybersecurity should be integrated across all divisions and at all levels. Cybercriminals do not recognize your internal organization or care about job titles but seek to exploit any weaknesses they discover.
 In late August of 2021, the
In late August of 2021, the 
 Frequently Asked Questions About the Kaseya Ransomware Attack
Frequently Asked Questions About the Kaseya Ransomware Attack

